Quantitative Nursing Research Articles 2022 Best
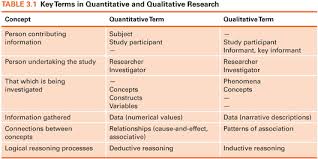
Identifying quantitative nursing research articles by using online databases. In this assignment, you will identify quantitative research study articles related to nursing problems as part of a Review of Literature
Quantitative Nursing Research Articles
Nursing quantitative research articles in a follow-up assignment Synthesis of the Review of Literature Using a Pinch Table. NO articles earlier than 2015 accepted. Identifies 4 appropriate study articles in a professional journal. Studies are quantitative. articles (for example: quantitative descriptive, correlational, comparative, quasi-experimental, or experimental designs). At least two studies must be prospective (data collected at the time of the study). The other two may be retrospective or prospective.
Quantitative Nursing Research Articles
Studies/ articles must be current, within 5 years and in English. Studies must logically relate to your topic, problem identification, and nursing practice. ‘Studies are NOT qualitative, a mixed-method study, a quality improvement study, a systematic review, meta-synthesis, meta-analysis, meta-summary, an integrative review, or a thesis or dissertation. No animal studies or pilot studies. Not a general information study without the elements of a study (e.g.: must include a review of literature and a methods section with results and discussion). Clinical Problem in Psychiatric or Mental Health Nursing is a Research Problem.
Quantitative Nursing Research Articles
In this assignment, you will identify quantitative research study articles related to nursing problems as part of a Review of Literature (Chapter 3 and 7). Follow the guidelines in Gray, Grove, & Sutherland (2017) Chapter 7 & 18 related to the Review of Literature. You will share your findings using a PINCH table in Module 4. Submitting your assignment, upload your four articles to the Instructions for Completing Your Assignment Step one: Choose the topic, identify a nursing clinical practice problem that you would like to explore. Psychiatric or Mental Health Nursing Research Problem briefly discuss the significance and identify the gap in the literature. (Why do you need to study this problem?)
Quantitative Nursing Research Articles
Search for at least FOUR nursing research articles that relate to your clinical problem using Academic Search Complete, CINHAL, PubMed, Google Scholar, or any other database that contains nursing research articles. Make note of your search strategy (keywords and databases used) to integrate into your next assignment. Your studies must be quantitative research articles (for example: quantitative descriptive, correlational or quasi-experimental or experimental designs). At least two studies must be prospective (data collected at the time of the study). The other two may be retrospective or prospective. https://youtu.be/yplWZs3dqNQ
Quantitative Nursing Research Articles
Your studies may NOT be a qualitative study, a mixed-method study, a quality improvement study, a systematic review, meta-synthesis, meta-analysis, meta-summary, or integrative review, or a thesis or dissertation. Studies/ articles must be current, within 5 years, and in English. Step four: Find the elements in your articles that are named in the PINCH Table identifies 4 appropriate study articles in a professional journal. Studies are quantitative. articles (for example: quantitative descriptive, correlational, comparative, quasi-experimental, or experimental designs). At least two studies must be prospective (data collected at the time of the study).
Quantitative Nursing Research Articles
The other two may be retrospective or prospective. current, within 5 years and in English. Studies must logically relate to your topic, problem identification, and nursing practice. ‘Studies are NOT qualitative, a mixed-method study, a quality improvement study, a systematic review, meta-synthesis, meta-analysis, meta-summary, or integrative review, or a thesis or dissertation. No animal studies or pilot studies. Not a general information study without the elements of a study (e.g.: must include a review of literature and a methods section with results and discussion).
Additional Files







