Tag Archives: environmental criminology
Routine Activity Theory. 2022 Best
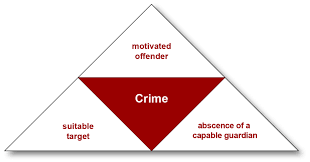
This assignment explores routine activity theory. The crime triangle (also known as the problem analysis triangle) comes straight out of one of the main theories of environmental criminology – routine activity theory.
Routine Activity Theory.
Watch Point/CounterPoint Routine Activities Theory(opens in a new tab) The theory described below is taken from the Center for POP article “Routine Activity Theory.”(opens in a new tab) The crime triangle (also known as the problem analysis triangle) comes straight out of one of the main theories of environmental criminology – routine activity theory. “Routine Activity Theory” provides a simple and powerful insight into the causes of crime problems. At its heart is the idea that in the absence of effective controls, offenders will prey upon attractive targets. To have a crime, a motivated offender must come to the same place as an attractive target.
Routine Activity Theory.
For property crimes the target is a thing or an object. For personal crimes the target is a person. If an attractive target is never in the same place as a motivate offender, the target will not be taken, damaged, or assaulted. Also, there are controllers whose presence can prevent crime. If the controllers are absent, or present but powerlessness, crime is possible. First, consider people who are influential in the lives of potential offenders. In the case of juveniles these might be parents, close relatives, siblings, peers, teachers, coaches, and other similarly placed individuals. In the case of adults these people may include intimate partners, close friends, relatives, and sometimes their children. https://youtu.be/z3_fnMjjb2Q
Routine Activity Theory.
These people are called “handlers” in routine activity theory. Crimes will take place where handlers are absent, weak, or corrupt. Next consider targets, or victims. Guardians try to protect targets from theft and damage and potential victims from attack and assault. Formal guardians include the police, security guards, and others whose job is to protect people and property from crime. Informal guardians include neighbors, friends, and others who happen to be in the same place as the attractive target. Parents, teachers, peers and others close to potential victims are also potential guardians. A target with an effective guardian is less likely to be attacked by a potential offender than a target without a guardian.
Routine Activity Theory.
If the guardian is absent, weak, or corrupt little protection is provided the target. Finally, consider places. Someone owns every location and ownership confers certain rights to regulate access to the site and behaviors of people using the site. The owner and the agents of the owner (e.g., employees) look after the place and the people using the place. Owners and their agents are called place managers. Place managers control the behavior of offenders and potential victims. Examples of place manager include merchants, lifeguards, parking lot attendants, recreation and park workers, janitors, and motel clerks.
Routine Activity Theory.
In the presence of an effective place manager, crime is less likely than when the manager is absent, weak or corrupt. All of the people in this theory use tools to help accomplish their criminal or crime control objectives. Tools that gang members use may include spray paint cans, guns, and cars. Offenders without access to tools are less likely to be able escape handlers, enter unauthorized places, and overcome victims, guardians, and managers. Guardians may use light to increase surveillance, engraving devices to mark property, and other devices to help reduce the chances of victimization. Place managers can use gates, fences, signs and other tools to regulate conduct.






